[Cell Interpretation Series] Uncover the mystery of Jurkat cells
Release time:
2023-02-10
Source:
Jurkat cell is a commonly used human T-cell leukemia cell line. This human T-cell leukemia cell line is a valuable resource for biological research. This cell line has the characteristics of rapid proliferation ability and easy culture, so it occupies an important position in biological research. This article will provide a detailed interpretation of the biological characteristics and applications of Jurkat cells to help readers better understand this important cell line.
newton optics
Intelligent imaging, one step in place!

Jurkat cell is a commonly used human T-cell leukemia cell line. This human T-cell leukemia cell line is a valuable resource for biological research. This cell line has the characteristics of rapid proliferation ability and easy culture, so it occupies an important position in biological research. This article will provide a detailed interpretation of the biological characteristics and applications of Jurkat cells to help readers better understand this important cell line.
01 What are Jurkat cells?
Jurkat cells are suspension cells. An immortalized human T-lymphocyte cell line for the study of acute T-cell leukemia, T-cell signaling, and the expression of various chemokine receptors, particularly HIV, for entry by susceptible viruses. It has a very wide range of applications in biological research, such as the application of Jurkat cells to study the M1-RNA of ribonuclease P, to explore the M1-RNA of anti-MHC class II molecular transcription activator (CIITA) to inhibit the expression of MHC class II molecules on the cell surface.
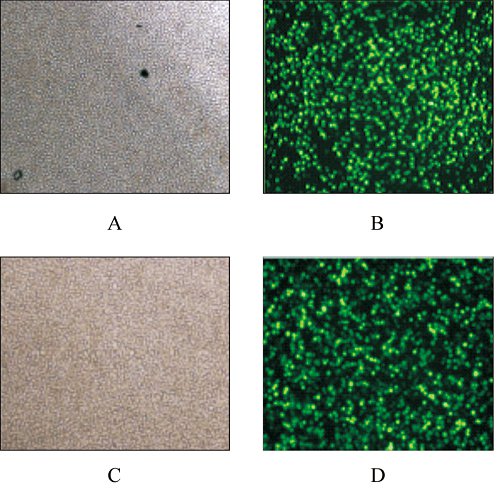
Fig. 4 fluorescence microscope detection diagram after recombinant plasmid is transfected into Jurkat cells note: a: white light detection diagram after cell transfection pEGFP-N3; B: fluorescence detection diagram after cell transfection pEGFP-N3: c: white light detection diagram after cell transfection pEGFP-N3-vMIP-I: d: fluorescence detection diagram after cell transfection pEGFP-N3-VMIP-I
Figure 4 The fluorescent microscopy diagrams in Jurkat cellstransfected with recombinant PlasmidsNote: A: Cells transfected with pEGFP-N3 observed in brightlighting; B: Cells transfected with pEGFP-N3 observed influorescent activation; C: Cells transfected withpEGFP-N3-vIIP-I observed in bright lighting; D: Cells transfectedwith pEGFP-N3-vMIP-I observed in fluorescent activation
02 Application scenario of Jurkat cell
Jurkat cells have a wide range of applications, mainly for the study of immunology and cancer biology. Specifically, they can be used in the following areas:
1. Cellular immune function research: Jurkat cells can be used to study the immune function of human T cells, including T cell activation, differentiation, induced cell death, etc;
2. Signal transmission research: "Jurkat cells can be used to study intracellular signal transduction pathways, such as T cell receptor signal transmission, cell cycle regulation, etc;
3. Drug effect research: Jurkat cells are a leukemia cell line that can be used to study cancer occurrence, metastasis, treatment and other issues.
The above are the main application scenarios that include but are not complete Jurkat cells, and different applications may exist in different fields.
03
Culture of Jurkat cells
After obtaining Jurkat cells, culture can be carried out according to the following steps:
1. Cell thawing: Thaw the frozen Jurkat cells into a culture dish;
2. Cell recovery: use RPMI 1640 medium to revert the cells;
3. Cell separation: After the cells aggregate to form a suspension, the cells are separated using 0.05% trypsin-EDTA;
4. Cell transplantation: Transplant the isolated cells into a new culture dish, and then add RPMI 1640 medium;
5. Cell culture: cells are cultured at 37 ℃ and 5% CO2, and the concentration and viability of cells need to be detected at regular intervals to understand the growth of cells.
6. Cell passage: Collect cells, centrifuge for 3-5min at 1000RPM, discard supernatant, add 1-2ml culture solution and blow evenly, and divide cell suspension into new dishes or bottles containing 8ml culture medium according to the ratio of 1:2 to 1:4.
7. Cell counting: In cell culture, the concentration and activity rate of cells need to be detected at a specific time. When using traditional blood cell plates to count, there are usually problems such as large errors and long time consumption. Newton optical cell counter can be a perfect solution to this problem, its high-throughput design can be a one-time detection of six cell samples in a minute, excellent optical system can effectively distinguish between cell impurities and debris interference, can quickly get very stable and reliable results.
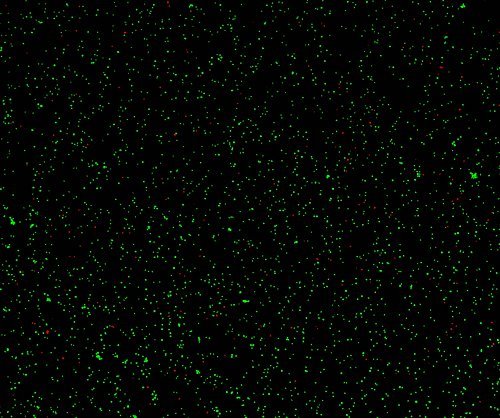

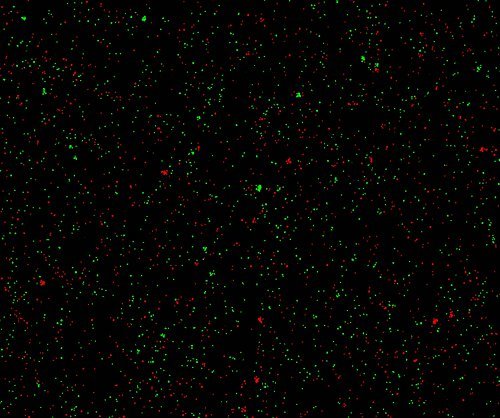
(Merge images of cells with different concentrations and different live rates under Newton optical CytoFlu fluorescence channel)
Key words:

National Advisory Service Hotline
Sales Consulting:86-15322243697(WeChat)
E-mail:sales@newtonoptic.com
R & D Center: Room 301, Floor 1, Building 1, No.38 Gaopu Road, Tianhe District, Guangzhou City, Guangdong Province

Follow Wechat Official Account
©2024 Guangzhou Newton Optics Research Institute Co., Ltd. All rights reserved